Are you also one of those people who have this question in your mind? Is CFC a greenhouse gas? If yes, then we are here for you to solve all your queries. Yes, CFC is a greenhouse gas. Actually, CFCs along with HCFCs (Hydrochlorofluorocarbons) act as very strong greenhouse gases, almost 10, 000 times more potent than carbon dioxide and water vapors. These are not only responsible for warming up the atmosphere of the earth but also, for depleting the ozone layer of the stratosphere which protects the earth from ultraviolet radiations of the sun. Chlorofluorocarbons or CFCs are classified as halocarbons i.e. the compounds comprised of carbon and halogen atoms. They are also sometimes referred to as Freons. They are the non-toxic, non-inflammable compounds that are used as refrigerants, solvents, etc., and also, in manufacturing aerosol sprays, packing materials, blowing agents for foams, etc. Let us study how CFC is a greenhouse gas and how it affects the environment.
What is a Greenhouse Gas?
A gas that contributes to the warming of the earth’s atmosphere by trapping thermal energy coming from the sun in the form of infrared radiation is known as a greenhouse gas.
There are certain naturally occurring greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, ozone, water vapors, etc. These gases help maintain the earth’s temperature favorable for the survival of various living organisms. These are responsible for sustaining various life forms on the earth. However, with the advent of various industries and human intervention in nature various unnatural greenhouse gases such as CFCs, HCFCs, etc. are also being dumped into the atmosphere. Also, the percentage of naturally occurring greenhouse gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, has also increased considerably in the atmosphere. Nature has its own cycle to pump in and take out various components into the environment. All the gases and other substances undergo cyclical changes due to which they always exist in balanced proportions in nature. However, human interference has disturbed the natural balance by inducing several unwanted components into the environment upsetting the entire ecosystem causing global warming and other severe climate change issues.
What is the Greenhouse Gas Effect?
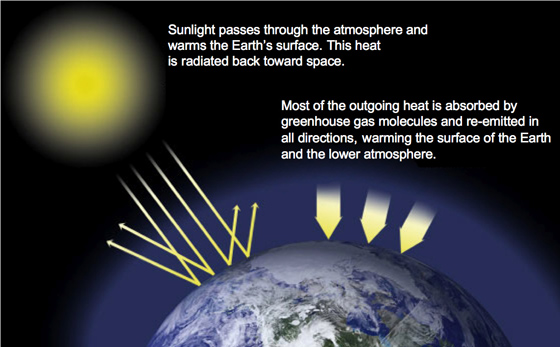
The greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapors, etc. those are naturally present in the atmosphere of the earth form an insulation cover around the surface of the earth. They trap the thermal energy coming from the sun and reflect them back to the earth’s surface, not allowing it to escape into space. This results in warming up the earth’s lower atmosphere and is referred to as the greenhouse gas effect.
Actually, the sun’s radiation reaching the earth is reflected back from the surface but it is not allowed to escape into the space instead it is absorbed by the greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, etc. which again reflect it back to the earth’s surface causing it to warm up. The wavelength of infrared radiations, which are responsible for the heat energy of the sun, is longer than the visible light due to which they are trapped while the visible radiations are allowed to get away easily. In the absence of the greenhouse effect, the temperature of the earth would drop around 30 degrees making it hostile for various life forms. However, the excessive accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere owing to human interference has resulted in major climate change issues such as rise in ocean levels, melting of glaciers, heat stresses, flooding, etc.
Why is CFC a Greenhouse Gas?
Chlorofluorocarbons are greenhouse gases as they contribute to trapping the thermal energy coming from the sun and do not letting it escape to space. Like other greenhouse gases, CFCs also absorb the infrared radiations being reflected by the earth’s surface. CFC gas fence in the heat energy and reflect it back to the earth’s surface causing it to get warm and thus, contribute to the rising of the overall temperature of the planet and eventually, climate change. CFCs are almost 10,000 times more potent as a greenhouse gas in comparison to other naturally occurring greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapors, methane, etc. Also, CFCs absorb thermal radiations at a wavelength different from those absorbed by CO2 or water vapors and thus, create a significant impact as a greenhouse gas. However, these are short-lived species that remain in the atmosphere for about 50-100 years while other greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide may last for a few centuries. However, even in their relatively short lifespan, CFCs are able to create a severe impact on the earth’s climate and also play a pivotal role in ozone depletion.
The CFCs have entered into the earth’s atmosphere owing to the human intervention also known as anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions. They were first used by Thomas Midgley as refrigerants, in 1928, and since then they have been widely used in different industries for a variety of purposes. However, the harmful effects of CFCs were soon noticed and efforts were made to reduce their emission. These steps finally lead to the signing of the Montreal Protocol in 1987 that banned the use of chlorofluorocarbons.
How Does CFC Destroy Ozone?
Since the advent of CFCs in the 1920s, an annual depletion of 3% has been observed in the ozone layer. In fact, chlorofluorocarbons have been categorized as ozone-depleting substances as they actively participate in the reactions causing depletion of the ozone layer. The CFCs are made up of chlorine, fluorine, and carbon atoms. They do not easily react with other substances present in the atmosphere. However, in the presence of the ultraviolet radiations of the sunlight, they split to form individual chlorine and fluorine atoms. These atoms react with the ozone present in the stratosphere and split the ozone molecule into oxygen and chlorine monoxide as per the following reaction: Cl + O3 —–> ClO + O2 When this ClO molecule comes in contact with another oxygen atom (O), it again splits up to release chlorine atom and form another oxygen molecule as indicated in the following reaction: ClO + O —-> Cl + O2 Therefore, the chlorine atom is again free to react with another ozone molecule indicating that a single chlorine atom is able to destroy hundreds of ozone molecules causing major damage to the ozone layer of the stratosphere.
Moreover, the CFCs do not even get dissolved in the rainwater and thus, remain in the atmosphere unchanged for several years causing significant damage to the ozone layer. The ozone depletion has been observed worldwide especially in the area over the South Pole, and also in some parts of North America, Europe, Asia, etc. This damage to the ozone layer causes the harmful UV-B radiations from the sun to enter into earth’s atmosphere. Usually, these radiations are reflected back into space by the protective ozone layer of the earth. Thus, depletion of the ozone layer has resulted in increased cases of skin cancer, loss of terrestrial and aquatic plant life, increased formation of surface ozone gas, etc.
What is CFC made of?
The major components of chlorofluorocarbons are chlorine, fluorine, and carbon atoms. When hydrogen atom replaces one or more halogen atoms they are known as hydrofluorocarbon (HFCs) or hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs).
All these are related compounds and are responsible for having similar effects on the atmosphere. Together, these compounds release large amounts of chlorine in the atmosphere that resulting in the depletion of the ozone layer. Also, being greenhouse gases they trap the thermal energy of the sun and hence, contribute to global warming and climate change.
Effects of Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) on Environment
The chlorofluorocarbons are used as refrigerants, as solvents, in aerosol sprays, etc. where they play different roles. However, when these CFCs enter the environment they act as pollutants that are responsible for degrading the overall quality of our environment. The CFCs being greenhouse gases are responsible for global warming and climate change and are, therefore, guilty of a number of natural calamities viz. melting of glaciers, floods, as well as exhausting animal and plant lives. These remain in the atmosphere for many years and throughout that time they act as strong pollutants. They are also responsible for the depletion of the stratospheric ozone layer of the earth where the CFCs dissociate to form chlorine which reacts with the ozone molecules to form oxygen molecules and chlorine monoxide. The chlorine atoms are again released in the atmosphere and are free to react with more ozone molecules thus, causing a severe impact on the protective ozone layer.
Conclusion
CFCs are greenhouse gases as they are capable of trapping the thermal energy received from the sun’s radiation. They absorb the heat and reflect it back to the surface of the earth without letting it escape into space. Any gas in the earth’s atmosphere that traps the heat energy from the sun is referred to as greenhouse gas, for example, CO2, methane, etc., and the overall rise in the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere owing to the presence of these gases is known as the greenhouse effect. CFCs are also responsible for depleting the ozone layer as they dissociate in the presence of sunlight and react with ozone molecules to form oxygen and chlorine monoxide. One chlorine atom may react with as many ozone atoms as possible thus causing a severe impact on the ozone layer. Happy Reading!!